Alan Neilan's blog of random stuff™
Project maintained by ANeilan Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
How to get Xfinity Stream to run on Linux (more specifically, Fedora Rawhide (or 39/40/41))
Introduction
A few years back, I came across an article that detailed how to go about getting Xfinity Stream to work on Linux, with instructions on how to do it on Debian-based distributions. Earlier this year, I switched my operating system over to Fedora (currently running Fedora Rawhide), and as a result, I needed a way to accomplish this on a Fedora-based system.
What you’ll need
In order to accomplish this, you’ll need a few things installed on your system:
- mock (this creates a virtual environment to build the package in, so you don’t have to clutter your system up with build dependencies)
sudo dnf install mock
- a text editor (whether that’s nano, vim, or vscode)
- a terminal (as one would imagine)
- glibc version 2.36 or newer (which encompasses Fedora versions stretching back to 37)
- quite a bit of spare time (takes about 2 hours to compile both architectures (i686 and x86_64))
- either chrome or firefox web browser
Getting started
First, you’ll want to make a directory to store the files you’ll be downloading, then navigate to that directory.
user@localhost:~$ mkdir temp_directory && cd temp_directory
Then, you’ll download the source rpm for glibc, and install the source rpm to your local rpmbuild folder.
user@localhost:~$ dnf download --source glibc
# in the case of Fedora Rawhide, I pulled this from https://koji.fedoraproject.org/koji/buildinfo?buildID=2575089. For fedora 39, 40, or 41, the version string may be different
user@localhost:~$ rpm -i glibc-2.40.9000-13.fc42.src.rpm
Next, you’ll want to open up the spec file in a text editor, and edit the following variables / lines:
%global baserelease- either increment it, or, as i do, add a .1 to the end
Patch26: glibc-xfinity-stream.patch- where you’ll put the patch that re-adds the functionality found in ChromeOS (which also uses glibc). To make sure it’s applied last, have it be whatever number is after the last patch number.
After this, you’ll likely want to add something to the changelog.
* Sat Oct 26 2024 Alan Neilan <email here> - 2.40.9000-13.1
- Add in patch that disables GLIBC_ABI_DT_RELR Check
- Allows xfinity stream to work w/ ChromeOS UA
Then, you’ll want to create the patch file in question in $HOME/rpmbuild/SOURCES/.
--- glibc-master-old/elf/dl-version.c
+++ glibc-master/elf/dl-version.c
@@ -362,7 +362,7 @@
/* When there is a DT_VERNEED entry with libc.so on DT_NEEDED, issue
an error if there is a DT_RELR entry without GLIBC_ABI_DT_RELR
dependency. */
- if (dyn != NULL
+ if (0 && dyn != NULL
&& map->l_info[DT_NEEDED] != NULL
&& map->l_info[DT_RELR] != NULL
&& __glibc_unlikely (!map->l_dt_relr_ref))
Finally, you’ll want to generate the newer source rpm to build from with the following command:
# if you're using a different version of fedora, you'll want to substitute it for the version here
user@localhost:~/rpmbuild$ mock -r /etc/mock/fedora-rawhide-x86_64.cfg --buildsrpm --spec SPECS/glibc.spec --sources SOURCES/
This will generate a source rpm file (src.rpm) in the following path (though the version number may be different based on which version of fedora you’re building this for):
/var/lib/mock/fedora-rawhide-x86_64/result/
You’ll want to copy this to your temporary directory, then build it against both 32-bit (i386/i686) and 64-bit (x86_64) architectures. It’s worth noting that it will take quite a bit of time to compile for both architectures. On my own system (Intel i5-8265U), it takes about an hour and change for each architecture to compile (for a combined time of ~2h10m).
user@localhost:~$ cp /var/lib/mock/fedora-rawhide-x86_64/result/glibc-2.40.9000-13.1.fc42.src.rpm ~/temp_directory/
# 64-bit (x86_64)
user@localhost:~$ mock -r /etc/mock/fedora-rawhide-x86_64.cfg temp_directory/glibc-2.40.9000-13.1.fc42.src.rpm
# 32-bit (i686/i386)
user@localhost:~$ mock -r /etc/mock/fedora-rawhide-i386.cfg temp_directory/glibc-2.40.9000-13.1.fc42.src.rpm
After the packages are finished compiling, you’ll want to copy both sets of packages to a directory.
user@localhost:~$ cp /var/lib/mock/fedora-rawhide-{i686,x86_64}/result/*.rpm ~/temp_directory/
Then, you’ll want to install the newer versions of the packages.
user@localhost:~$ cd temp_directory
user@localhost:~$ sudo dnf upgrade ./*.rpm
At this point you’ll want to restart your computer, which will allow the newer version of glibc to take effect.
user@localhost:~$ sudo systemctl reboot
Browser setup
Once your computer is back up and running, you’ll want to fetch a Chrome OS system image. You’ll want to grab one from the atlas codename, as that’s the one I used for this. Once it’s downloaded, you’ll need to unpack the zip file like so.
user@localhost:~/Downloads$ unzip chromeos_16002.60.0_atlas_recovery_stable-channel_mp-v6.bin.zip
Archive: chromeos_16002.60.0_atlas_recovery_stable-channel_mp-v6.bin.zip
inflating: chromeos_16002.60.0_atlas_recovery_stable-channel_mp-v6.bin
After it’s unpacked, you’ll want to use the included Gnome disk utility to mount the disk image
After attaching the system image (in this case chromeos_16002.60.0_atlas_recovery_stable-channel_mp-v6.bin), a few partitions on that system image will be mounted automatically.
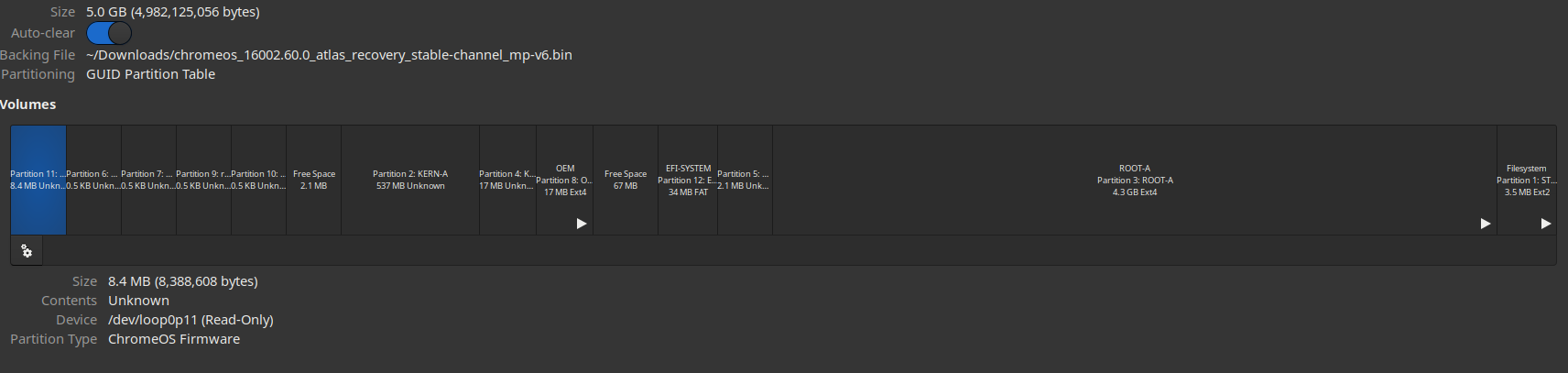
Notice the partition labeled “Root-A”, that partition will be mounted at the path /run/media/$username/ROOT-A/. You’re goint to want to copy the following file opt/google/chrome/WidevineCdm/_platform_specific/cros_x64/libwidevinecdm.so from that mount point, to either of the following locations depending on which browser you’re going to be using to watch Xfinity Stream.
- Firefox
$HOME/.mozilla/firefox/${whatever your firefox profile name is}/gmp-widevinecdm/${whatever version it ends up being (currently 4.10.2830.0)}/- Note: you’ll need to go into firefox’s settings to check the box that enables EME (Encrypted Media Extensions) which downloads the default
libwidevinecdm.sobefore replacing it with the one from the Chrome OS system image
- Note: you’ll need to go into firefox’s settings to check the box that enables EME (Encrypted Media Extensions) which downloads the default
- Google Chrome
/opt/google/chrome/WidevineCdm/_platform_specific/linux_x64/
The next steps involve getting Xfinity Stream to think you’re on a Chrome OS device.
- Firefox
- go into
about:config - create a new string variable titled
general.useragent.override - set it to the following:
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; CrOS x86_64 10066.0.0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/129.0.0.0 Safari/537.37 - restart your browser window to allow it to take effect.
- sign into Xfinity Stream using your Comcast/Xfinity account details
- go into
- Google Chrome
- go to the Xfinity Stream website
- open your Chrome Developer Tools
- click on the three dotted line
- hover over
more tools - select
network conditions - uncheck
use browser defaultunder user agent. - select
Chrome - Chrome OSas the user agent - sign into Xfinity Stream using your Comcast/Xfinity account details
Conclusion
These steps should work, so long as Xfinity/Comcast doesn’t try and institute any changes to the backend that locks out Chrome OS users. Hope this helps.